Detailed Design
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to produce a design document
based on business requirement and functional requirements specified in the Analysis
phase. The document presents the detail design of the back end database along with
class diagrams and Interface design.
1.0
Project Description and Scope
Groceries-To-Go is an online grocery pick-up service. Customers can go to our site
to order groceries, pay for it online, and schedule an exact time to pick up their
groceries - already bagged and ready to go. We would have partnerships with local
grocery chains that provide the freshest foods and produce.
2.0 Detailed Design
2.1. Overview of Application Changes
Users will be able to join groceriestogo.com facebook account and follow us on our
twitter account.
2.2 Significant Algorithm
The major functionality of
the application is to allow users to order products and schedule pick up time. The
sudo code below explains the ordering and time scheduling process.
get buyer data and shopping cart data from web forms
insert buyer data into buyer table
BEGIN WORK
start order by creating row in orders table
get current orderId
for each item desired
check available
inventory
if inventory is available
write item to order table
decrement inventory
allow user to
set the pickup time
else
set error variable to true
endif
end for loop
if error variable is true
ROLLBACK
else
get
total for items for the order update orders table
COMMIT
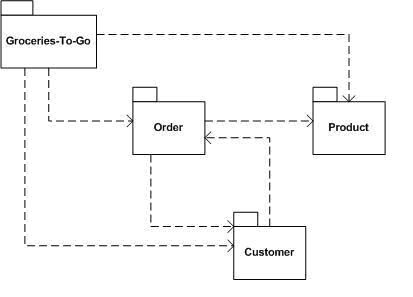
2.2.1 The package diagram below shows the pickup procedure.
2.2.2 The following class diagram shows the grocery pick up class diagram.
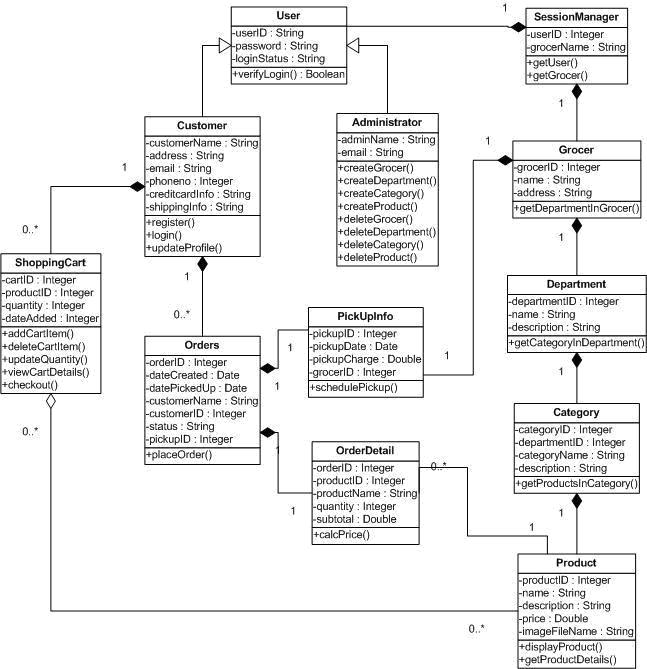
2.2.3 Descriptions
a.
User
This class handles all user actions. The User class is the super class of Customer
and Administrator. It includes the private methods to verify the login of the user.
The verifyLogin() method is called when the user clicks the "Sign In" button on
the Login.aspx Web form. It returns true if the login is successful, false if it
is not.
b. SessionManager
The SessionManager class supports the User’s required
operations like getUser() and getGrocer(). The getUser method is called when the
user information needs to be displayed. The getGrocer() method is used to get an
existing participating grocer. When the user needs to get a product, the system
has to start from the Session Manager and navigate down to the Product class.
c.
Administrator
This class handles the Administrator actions. It inherits all the User class responsibilities
and its functions. The functions createGrocer(), createDepartment(), createCategory(),
createProduct() are called when the administrator has to create/add a new grocer,
department, category, or product respectively to the database. Similarly, operations
like deleteGrocer(), deleteDepartment(), deleteCategory() and deleteProduct() are
called when deleting a grocer/department/category/product respectively from the
database. For these delete operations to be valid there should be at least one grocer,
department, category and product already existing in the database.
Conditions for createProduct Operation
·
Purpose: To enable Administrator to create and add new products
to the database.
·
Pre Condition: Administrator
must be logged in to be able to create a new product. Also, the department and/or
category to which the new product is to be associated should exist in the database.
·
Post Condition:
Product will be added to the corresponding department and/or category.
·
Input: Administrator
will enter the name and necessary details to create a new product and click "Add"
button to complete the action.
·
Output: After
the action, the changes to the catalog will be updated and saved and a message will
be displayed accordingly.
d. Customer
This class handles the customer actions. It inherits all the User class responsibilities
and its functions. The updateProfile() method is called when customer wants to edit,
update and save his/her personal information on the website for future use. But
to update profile, customer must register and login through the Register.aspx and
Login.aspx Webpage which uses the register() and login() methods.
Conditions for Login Operation
·
Purpose: This
is implemented to enable user authentication. A valid user account must be used
for an existing customer.
·
Pre Condition: The
customer should be registered with website and should have a valid userid and password.
·
Post Condition:
Customer will be able to browse through the website.
·
Input: The
customer can login to the Groceries-To-Go website by entering his user name and
password.
·
Output: The
system will verify that the login name matches the login password. If the user name
or password is invalid, the appropriate error message will be indicated and the
user will be requested to re-enter user name and password. If the user inputs are
valid, the main page will be displayed.
e. Grocer
This class has all grocers that have partnered with Groceries-To-Go. This class
has a private method called getDepartmentInGrocer() which is used get all the departments
from the grocer. A grocer may contain zero or more departments.
f. Department
This class has all different department lines from produce to health &
beauty. This class has a private method called getCategoryInDepartment() which is
used get all the categories in a particular department. A department may contain
zero or more categories and the corresponding products.
g. Category
This class has all different categories for the corresponding departments.
This class has a private method called getProductsInCategory() which is used get
all the products belonging to a particular category and department. A category can
belong to one or more departments. Also, a category can contain zero or more products.
h. Product
This class represents a collection of products of a particular category and/or
department. The displayProduct() and getProductDetails() method are called when
the user clicks on a product or on the "Search" button on the Search.aspx Web form.
The displayProduct() method is used to retrive image of the product and getProductDetails()
method retrieves its details as a data set whenever a customer clicks on the product.
A product can belong to one or more departments and/or categories.
i. ShoppingCart
ShoppingCart class has all the products that are added by a customer to buy.
The addCartItem() and deleteCartItem() methods are called when customer performs
actions like "Add to Cart" and "Delete" of products on the ShoppingCart.aspx Webpage.
The updateQuantity() method is called when Customer clicks "Update" button on ShoppingCart.aspx
Webpage to increase or decrease the number of products in the cart. Also, viewCartDetails()
method is called when customer clicks on the "View Details" button to see a summary
of the cart. It will display the summary only when cart is not empty, else it will
display "Your Cart is empty."
Conditions for addCartItem Operation
·
Purpose: This
is implemented so the customer can add products to shopping cart while searching
or browsing catalog.
·
Pre Condition: The customer must be logged
in to add a product to the cart.
·
Post Condition: Product will be added to the
shopping cart.
·
Input: When
customer finds the products he wants, he adds them to the shopping cart by clicking
on the "Add to Cart" button.
·
Output: Product
will be added to the shopping cart and the system will store and keep track of the
information of products that have been added into shopping cart.
Conditions for Checkout Operation
·
Purpose: To allow
customer to buy the products added to the shopping cart.
·
Pre Condition: Customer must be logged in and
must have at least one item in shopping Cart to be able to checkout and place the
order.
·
Post Condition:
Customer will be successfully checked out and will be able to edit his profile information
and place order.
·
Input: When
the customer finishes shopping, he requests to checkout by clicking "checkout" button
on ShoppingCart.aspx page.
·
Output: If the
payment information of this customer already exists, the system prompts the customer
to review or input a new one. If the credit card is valid, the order form will be
processed by the system and checkout is complete.
j. Orders
This class will store all information regarding the orders made by each customer.
The placeOrder() method is called when customer clicks on the "Place Order" button
on the Order.aspx Web form. It returns true if the order is placed successfully,
false if it is not.
The "Place Order" button will be enabled only when customer has a valid shopping
cart and has entered valid personal, billing and pick-up details.
Conditions for placeOrder Operation
- Purpose: To allow
customer to place an Order for buying the products added to the shopping cart.
- Pre Condition: Customer
must be logged in and must have at least one item in shopping Cart to be able to
place the order. Pick-up date and time also needs to be specified. In terms of payment,
customer should have correct profile information and valid Credit Card details entered
into the system.
- Post
Condition:
Customer will be successfully able to place the order.
- Input: When
the customer finishes shopping and has determined a designated date and time to
pick-up items, he requests to place an order by clicking "Place Order" button on
the Order.aspx page.
- Output: If the
profile information, payment information the credit card of this customer is valid,
the order form will be processed by the system and order is placed.
k. PickUpInfo
This class handles the pick-up information regarding every customer and their orders.
The schedulePickup() method is called when customer schedules a pick-up date and
time and clicks the "Schedule Pick-Up" button on the Order.aspx Webpage.
l. OrderDetail
This Class handles details regarding every order that the customer makes. The calcPrice()
method is called to calculate the total amount of the order placed. The method also
calculates the total amount of the order including pick-up charges.
3.0 Data Structure (Data
Models and Tables )
3.1 ER Diagram
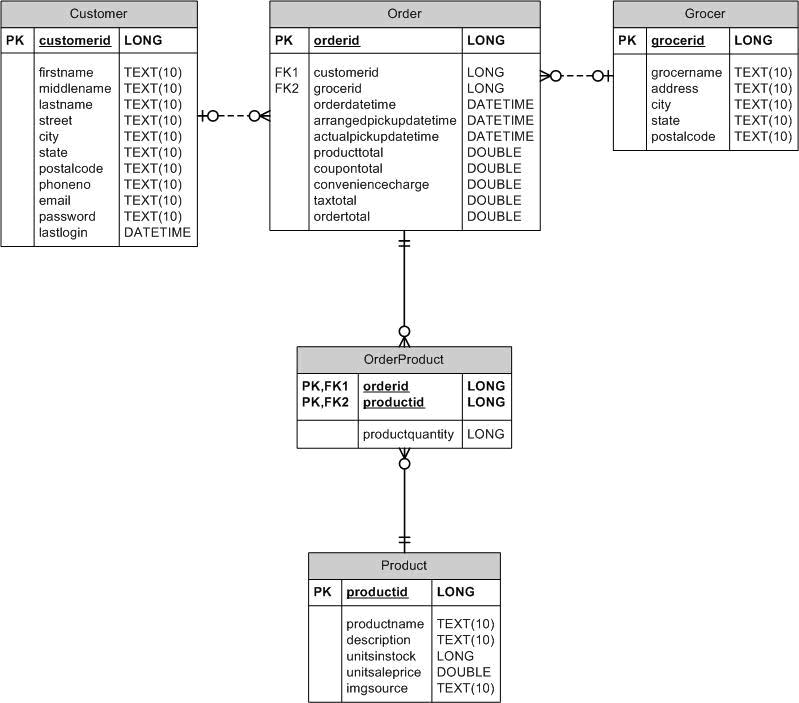
3.2 DML Statements
DROP TABLE OrderProduct;
DROP TABLE Order;
DROP TABLE Product;
DROP TABLE Grocer;
DROP TABLE Customer;
CREATE TABLE Customer (
city VARCHAR(50),
customerid
IDENTITY,
email
VARCHAR(50),
firstname
VARCHAR(50),
lastlogin
datetime,
lastname
VARCHAR(50),
middlename
VARCHAR(50),
password
VARCHAR(50),
phoneno
VARCHAR(50),
postalcode
VARCHAR(50),
state
VARCHAR(50),
street
VARCHAR(50)
);
ALTER TABLE Customer
ADD PRIMARY KEY (customerid);
CREATE TABLE Grocer (
address
VARCHAR(50),
city
VARCHAR(50),
grocerid
IDENTITY,
grocername
VARCHAR(50),
postalcode
VARCHAR(50),
state
VARCHAR(50)
);
ALTER TABLE Grocer
ADD PRIMARY KEY (grocerid);
CREATE TABLE Product (
description
VARCHAR(50),
imgsource
VARCHAR(50),
productid
IDENTITY,
productname
VARCHAR(50),
unitsaleprice
double DEFAULT 0,
unitsinstock
int DEFAULT 0
);
ALTER TABLE Product
ADD PRIMARY KEY (productid);
CREATE TABLE Order (
actualpickupdatetime
datetime,
arrangedpickupdatetime
datetime,
conveniencecharge
double DEFAULT 0,
coupontotal
double DEFAULT 0,
customerid
int DEFAULT 0,
grocerid
int DEFAULT 0,
orderdatetime
datetime,
orderid
IDENTITY,
ordertotal
double DEFAULT 0,
producttotal
double DEFAULT 0,
taxtotal
double DEFAULT 0
);
ALTER TABLE Order
ADD PRIMARY KEY (orderid);
CREATE TABLE OrderProduct
(
orderid
int DEFAULT 0,
productid
int DEFAULT 0,
productquantity
int DEFAULT 0
);
ALTER TABLE OrderProduct
ADD PRIMARY KEY (productid, orderid);
ALTER TABLE OrderProduct
ADD FOREIGN KEY (productid) REFERENCES
Product(productid) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE CASCADE;
4.0 Interface Design
4.1 Improved high fidelity wireframe of groceriestogo.com
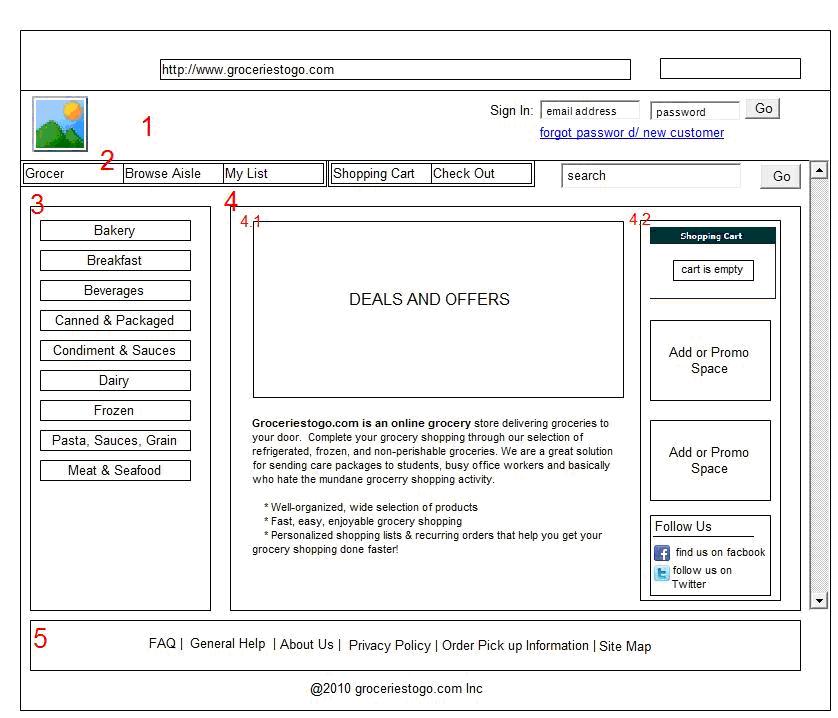
Improved high level wireframe for groceriestogo.com
4.2 Mobile
phone interface for groceriestogo.com
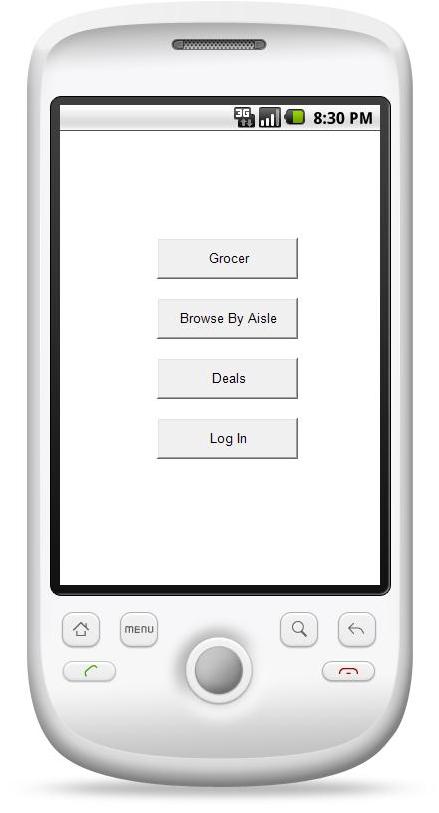
4.3 Medium fidelity prototype for groceriestogo.com
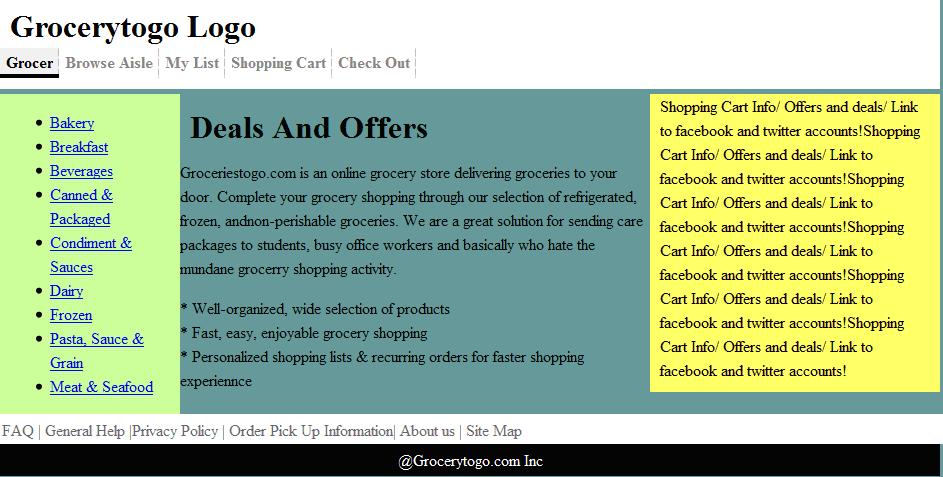
Web interface
will coded using XHTML 1.0 STRICT. This standard is based on W3C.
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd">
The
Mobile
site will be coded using XHTML MP 1.0
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//WAPFORUM//DTD XHTML Mobile 1.0//EN" "http://www.wapforum.org/DTD/xhtml-mobile10.dtd">
4.4 Content will be styled
using an external CSS style sheet. Basic CSS for the site is as follows:
body{
margin:0;
padding:0;
line-height: 1.5em;
background-color:#699;
}
#maincontainer{
width: 940px; /*Width of main container*/
margin: 0 auto; /*Center container on page*/}
#topsection{
background:#FFF;
height: 90px; /*Height of top section*/
}
#contentwrapper{
float: left;
width: 100%;
}
#contentcolumn{
margin: 0 290px 0 180px; /*Margins for content column. Should be "0 RightColumnWidth
0 LeftColumnWidth*/
background-color:#699;
}
#leftcolumn{
float: left;
width: 180px; /*Width of left column in pixel*/
margin-left: -940px; /*Set margin to that of -(MainContainerWidth)*/
background: #C8FC98;
}
#rightcolumn{
float: left;
width: 290px; /*Width of right column*/
margin-left: -290px; /*Set left margin to -(RightColumnWidth)*/
background: #FDE95E;
}
#footer{
clear: left;
width: 100%;
background: black;
color: #FFF;
text-align: center;
padding: 4px 0;
}
#bottomnav{
clear: left;
width: 100%;
background:white;
color:#666;
text-align:left;
padding: 4px 2px 2px 2px;
}
#bottomNav a{
color: #FFFF80;
}
.innertube{
margin: 10px; /*Margins for inner DIV inside each column (to provide padding)*/
margin-top: 0;
}
</style>
5.0 Navigation Schemes
Top Navigation: Main Navigation
Grocer | Browse Aisle | My List | Shopping Cart | Check Out |
Left Horizontal Navigation: Quick links
to list of different grocery types
Bakery | Breakfast| Beverages | Canned
& Packaged | Condiment & Sauces | Dairy | Frozen | Pasta, Sauces, Grain
| Meat & Seafood
Bottom Navigation: Information and help
FAQ | General Help |Privacy Policy | Order Pick Up Information| About us | Site
Map
Mobile Phone Navigation:

5.1 Information Architecture

5.2 Page Content Information
1.
Home (http://www.groceriestogo.com): Users accessing the site using mobile phone will be redirected
to the mobile interface.
a.
Logo
b.
High Level Navigation (Main Navigation)
c.
Search Button
d.
Sub Navigation
e.
Deals
f.
Company Info
g.
Add or Promotion
1.1
Log In: User can log or register with the site.
1.2
My Account: My Account will display past purchases or
activities. Your available coupons or favorite items etc.
2
Grocer: The grocer page will provide user with the list
of grocers they can do their shopping from.
3
Browse Aisles: List of different types of groceries.
3.1
General Grocery:
3.2
Produce Stand:
3.3
Meat & Seafood:
3.4
The Daily:
3.5
Health & Beauty:
3.6
Wine & Spirits:
4
My List: List of products
5
Shopping Cart: Your Shopping cart or list of products
you just bought.
6
Check Out: Check out or finalize purchase
6.1
Schedule Pickup: In this page user schedules a pick up
time for their order.
6.2
Order Summary/Print Receipt: Summary of the order. Here
user can either save and print the receipt of the order.
7
FAQ: Answers to most frequently asked questions by the
users.
8
General Help: Help and support generally with technical
aspect of the website.
9
Privacy Policy: Describes the privacy policy of groceriestogo.com.
10
Shopping Information: Information to users about shopping
with groceriestogo.com
11
About us: Allows user to look at the company profile.
11.1
Mission
: The mission
statement of the organization.
11.2
Partners: Shows
the list of grocers, the organization partners with.
12
Site Map: Displays the map of the site.
6.0 Testing Consideration - Usability Testing
scenarios
6.1 Executive
Summary
The following paragraphs contain the methodology that our team will use in order
to carry out an informal usability test for our website. The purpose of the usability
test is to identify possible anomalies linked to the website’s interface that could
hinder potential users from our target audience from accomplishing tasks associated
with purchasing products.
6.2 Document
Overview
Usability test is a vital step to improve the
ICA
’s online registration system efficiency. According to
Dumas and Redish, “Usability Testing is
an applied form of experimentation used by developers to test whether the product
they develop is usable by the intended user population to achieve their tasks.”
The objective of the usability test will be to identify users’ difficulties in performing
tasks. The reasons for such difficulties can be a consequence of navigation errors
linked to misinterpretation of the interface and/or system defects.
The usability test of our website’s online purchase system will be carried out with
the participation of a pool of ten (10) individuals. The chosen individuals who
will carry out the usability test represent potential clients, having average technological
skills. After the test have been carried out and analyzed, our team will be able
to make modifications to the system and improve its user interface and efficiency.
We will carry out the usability tests in an informal manner. We will give the users
several tasks to perform while “thinking aloud”, in a neutral environment. Team
members will be taking notes and will not influence the test participants while
they are performing their tasks.
6.3 Methodology
In order to conduct usability tests, it is important to select a list of heuristics
or principles and test the system’s user interface to identify usability issues
that could mislead users. We selected a list of common used heuristics directly taken
from
http://www.useit.com/papers/heuristic/, developed by Jakob Nielsen.
They have been reproduced here:
-
Visibility of system
status (making
sure the system provides adequate feedback to the user while performing the task)
-
Match between system
and the real world
(using concepts, words and phrases that are clear and understandable to the user)
-
User control and
freedom (allow
the user to go back and forth between different steps , editing input and exiting
the system)
-
Consistency and standards (use of the same terminology
and wording in every page)
-
Error prevention (providing feedback about
incorrect or invalid input)
-
Recognition rather
than recall
(provide a clear path-finding layout)
-
Flexibility and efficiency
of use (are
there redundancies that prevent users from accomplishing tasks in a quick and efficient
manner)
-
Help users recognize,
diagnose, and recover from errors
(providing feedback and possible solutions)
-
Simplicity
(user perceives the system is easy to use)
Participants will be at least 18 years old (for legal purposes). The main characteristics
for their eligibility are their belonging to our target audience and possessing
average technology skill level. Participants do not need to be familiar with the
evaluated tasks and do not need to have a specific background.
6. 3.2 Roles
Our team identified three different roles for the purpose of our test:
-
Test facilitator:
in charge of informing the participants of the tasks they will have to accomplish,
provide instructions before the test and give the legal consent form. If the user
is completely stuck during the test, the test facilitator will ask questions about
why they are experiencing difficulties.
-
Data logger:
team members in charge of observing the participant while effectuating the tasks
and writing down test progression, results and feedback.
-
Test participant:
person who carries out the tests. They will be asked to sign the legal consent form
authorizing our tem to perform the usability tests. The participant will never have
used the system previously and will perform typical tasks, bringing any difficulties
they may have to the team’s attention. This person will provide constant feedback
by “thinking aloud” and will at the end give an overall evaluation of the website’s
user interface by filling out a survey related to the heuristics listed in the beginning
of this section.
6.3.3 Persona
The team has developed the following persona which is meant to be representative
of persons who visit our website with the intent of buying a product.
John Walkins is a 38 year old manager at Harley-Davidson
Financial Services. He is a very busy
professional, experienced in the management and financial fields. John earns an
average salary of $70.000 a year. If John is still single, his job takes most part
of his time schedule. As he prefers spending his precious time with other priorities,
John often shops for groceries online. In his case, this has been the most effective
way of realizing this house chore in order to save time. On the other hand, he hates
the need of going home earlier to wait for the company’s delivery service. Actually,
he would like to avoid such step. John has also average technological skills.
6.3.4 Scenarios
Test participants will be asked to carry out the following five typical tasks while
standing in for the persona created above.
·
Find out where to register or log in.
·
Go back and change input (i.e: name, address, etc…) before finalizing the registration.
·
Find out where to contact us for customer assistance.
·
Find different categories of products.
·
Understand our concept (of picking-up own groceries)
·
Go through the process up to the payment step, where the usability test will end.
Contributions
|
Name
|
Contribution
|
|
Allan Sievert
|
Database Design, UML, Class Design, Class Description
Algorithm, Documentation, Information Architecture
|
|
Sumit Mukhia
|
Documentation,
Interface Design, Algorithem Wireframe, Page Content Information
|
|
Gian Avolio
|
Usability,
System Analysis, Design, Testing Consideration and Interface Design
|